In the world of personal finance and investment, mutual funds are among the most popular tools for growing wealth. They are versatile, accessible, and suitable for both novice and experienced investors. However, to make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of mutual funds, it is essential to understand their basics. This comprehensive guide will delve into what mutual funds are, how they work, their types, benefits, risks, and tips for investing wisely.
What Are Mutual Funds?
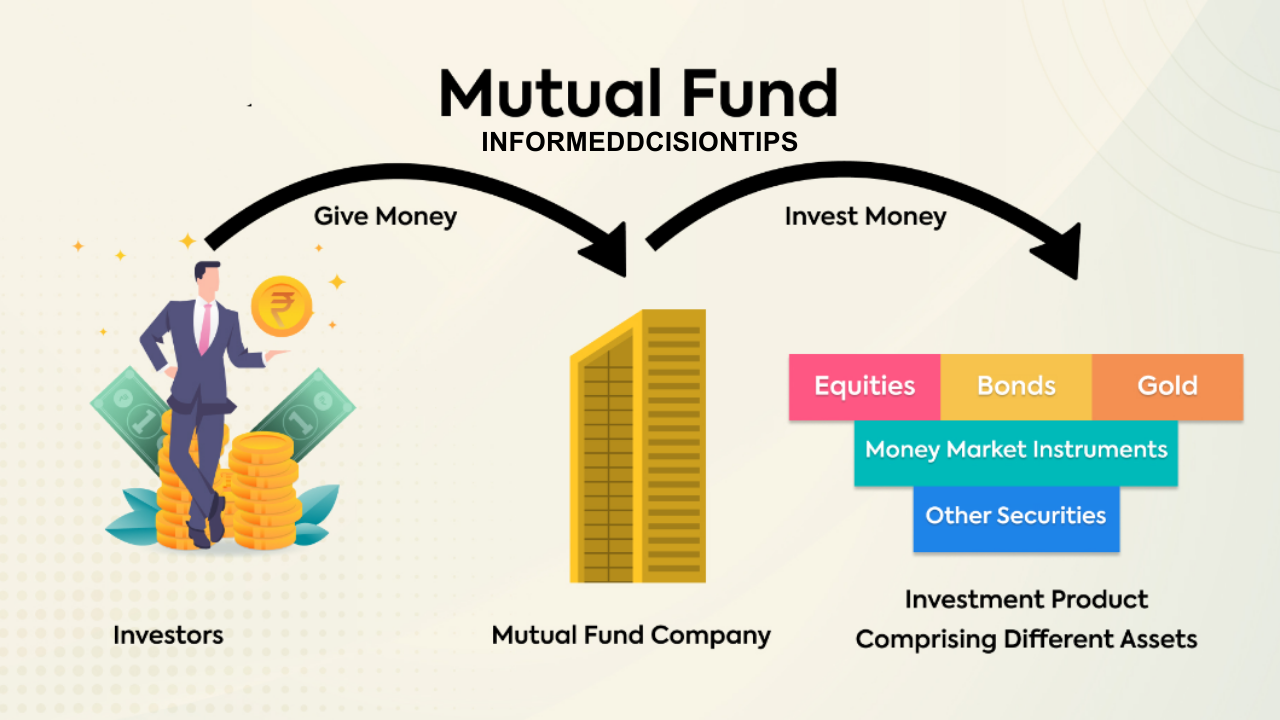
A mutual fund is a pooled investment vehicle managed by professional fund managers. It collects money from multiple investors and invests it in a diversified portfolio of assets, including stocks, bonds, money market instruments, and other securities. The primary goal is to provide investors with a return that matches the fund’s objectives.
Investors in a mutual fund own units, which represent a proportionate share of the fund’s holdings. The value of these units fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying assets, and this value is known as the Net Asset Value (NAV).
How Do Mutual Funds Work?

- Pooling Money: A mutual fund collects money from a group of investors who share a common investment objective.
- Professional Management: A professional fund manager or a team of managers oversees the fund’s investments, making decisions about which securities to buy, hold, or sell.
- Diversification: The pooled money is invested across a wide range of assets to reduce risk. Diversification ensures that poor performance in one asset class does not significantly impact the overall portfolio.
- Returns: Investors earn returns through dividends, interest, or capital appreciation of the underlying assets. These returns can be reinvested or distributed, depending on the type of fund.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds can be broadly classified based on their structure, investment objectives, and asset classes:
- By Structure:
- Open-Ended Funds: Investors can buy and sell units at any time based on the NAV.
- Closed-Ended Funds: These have a fixed number of units and are traded on stock exchanges. Units can only be bought during the initial offer period.
- Interval Funds: A hybrid of open-ended and closed-ended funds, allowing purchases or redemptions at specific intervals.
- By Investment Objective:
- Equity Funds: Primarily invest in stocks to achieve capital appreciation.
- Debt Funds: Focus on fixed-income securities like bonds to provide regular income.
- Hybrid Funds: Combine equity and debt investments to balance risk and return.
- Money Market Funds: Invest in short-term debt instruments for liquidity and safety.
- By Asset Class:
- Sector Funds: Invest in specific industries like technology, healthcare, or energy.
- Index Funds: Mirror the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500.
- International Funds: Focus on assets outside the investor’s home country.
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
- Professional Management: Mutual funds are managed by experienced professionals who have the expertise to analyze markets and make informed investment decisions.
- Diversification: By investing in a wide array of assets, mutual funds reduce the risk of significant losses.
- Liquidity: Open-ended mutual funds offer high liquidity, allowing investors to buy or redeem units at their convenience.
- Affordability: Mutual funds allow small investments, making them accessible to individuals with limited capital.
- Transparency: Regular updates on portfolio holdings, performance, and fund objectives provide investors with transparency.
- Tax Benefits: Certain mutual funds, such as Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), offer tax advantages under specific regulations.
Risks Associated with Mutual Funds
While mutual funds offer several advantages, they are not without risks. Investors should be aware of the following:

- Market Risk: Mutual fund returns are subject to market fluctuations, which can impact the value of investments.
- Credit Risk: Debt funds may face the risk of issuers defaulting on their obligations.
- Liquidity Risk: Some funds may face challenges in selling assets quickly without impacting their value.
- Expense Ratio: The costs associated with managing the fund, known as the expense ratio, can affect returns.
- Inflation Risk: The purchasing power of returns may diminish over time due to inflation.
Factors to Consider Before Investing
- Investment Goals: Identify your financial goals, whether it’s wealth creation, income generation, or capital preservation.
- Risk Appetite: Assess your risk tolerance to choose funds that align with your comfort level.
- Time Horizon: Determine your investment period. Equity funds are better for long-term goals, while debt funds suit short-term objectives.
- Fund Performance: Analyze the fund’s historical performance but remember that past results do not guarantee future outcomes.
- Expense Ratio: Choose funds with lower expense ratios to maximize returns.
- Fund Manager Expertise: The skills and experience of the fund manager play a crucial role in the fund’s performance.
Steps to Invest in Mutual Funds
- Define Your Goals: Clarify your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
- Choose a Fund: Research and select a fund that aligns with your goals.
- Complete KYC: Fulfill Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements to invest in mutual funds.
- Select an Investment Mode: Decide between a one-time investment (lump sum) or periodic investments through a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP).
- Monitor Your Investments: Regularly review the performance of your funds and make adjustments if necessary.

Common Myths About Mutual Funds
- “Mutual Funds Are Only for Experts”: Mutual funds are designed for all investors, regardless of their expertise.
- “They Guarantee Returns”: Mutual funds do not guarantee returns; they are subject to market risks.
- “They Are Too Risky”: The risk level varies by fund type. Debt funds are less risky than equity funds.
- “You Need a Lot of Money to Invest”: Many mutual funds allow investments as low as $10 or equivalent.
- “You Lose Control Over Your Money”: Investors can redeem their investments at any time in open-ended funds.
Mutual funds are an excellent investment option for individuals seeking professional management, diversification, and convenience. However, like any investment, they come with risks. To make the most of mutual funds, it’s vital to understand their basics, evaluate your financial goals, and choose funds that align with your needs.
By staying informed and proactive, you can harness the potential of mutual funds to achieve your financial aspirations. Whether you’re saving for retirement, a child’s education, or simply building wealth, mutual funds can be a valuable component of your investment portfolio.
Leave a Reply