Digestive issues like bloating and gas are common problems that can cause discomfort and affect daily life. While occasional bloating and gas are normal, persistent symptoms may indicate underlying digestive imbalances. Understanding the causes and implementing effective remedies can significantly improve digestive health and overall well-being.
This guide explores the causes of bloating and gas, lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, home remedies, and medical treatments to manage and prevent digestive discomfort effectively.
Understanding Bloating and Gas
What is Bloating?
Bloating refers to a feeling of fullness, tightness, or swelling in the abdomen, often accompanied by pain or discomfort. It occurs when excess gas builds up in the digestive tract, leading to pressure and distension.
.png)
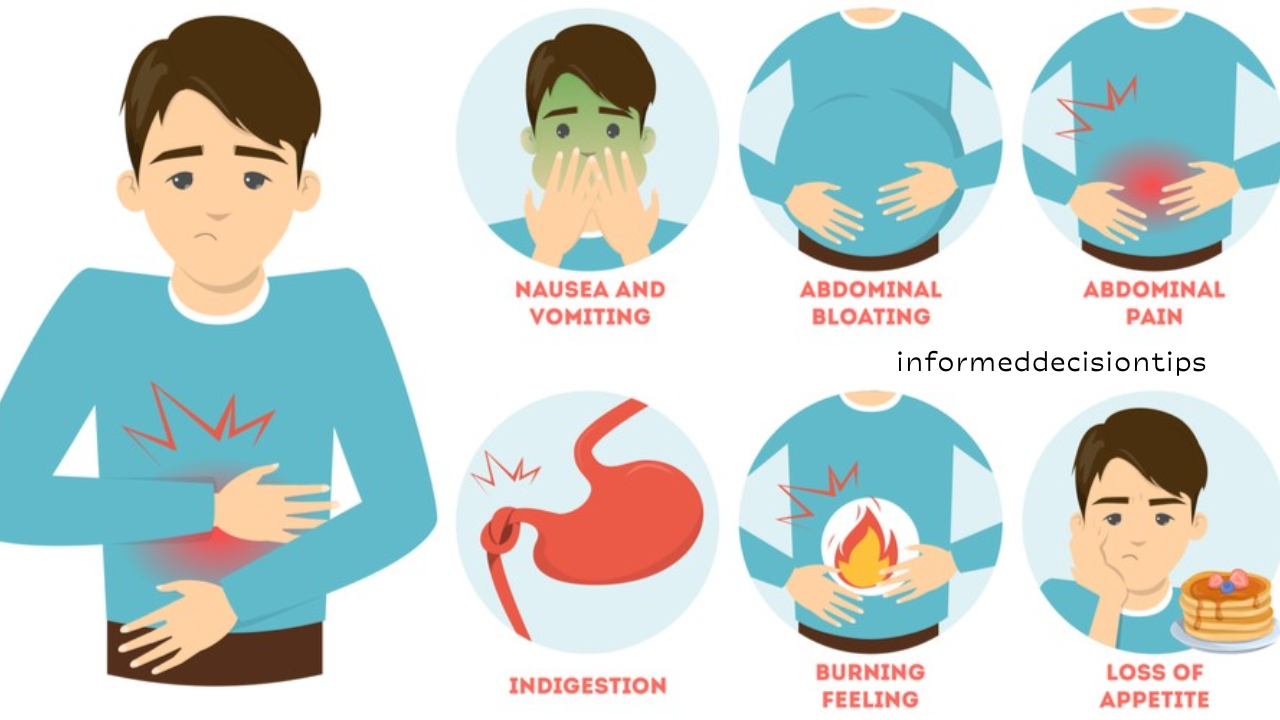
What Causes Gas?
Gas in the digestive system is primarily caused by swallowed air and the fermentation of undigested food by gut bacteria. It is released through burping or flatulence. While it is a natural process, excessive gas can lead to bloating, cramps, and embarrassment.
Common Causes of Bloating and Gas
1. Dietary Habits
- Overeating or eating too quickly
- Consuming carbonated drinks (soda, beer)
- High intake of processed and greasy foods
- Eating gas-producing foods like beans, lentils, broccoli, and cabbage
2. Food Intolerances and Sensitivities
- Lactose intolerance: Inability to digest lactose in dairy products
- Gluten sensitivity: Adverse reactions to gluten in wheat, barley, and rye
- Fructose malabsorption: Difficulty absorbing fructose in fruits and sweeteners
3. Gut Health Issues
- Imbalance of gut bacteria: Overgrowth of harmful bacteria can cause excess gas
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A disorder affecting gut motility and digestion
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO): Excess bacteria in the small intestine causing bloating
4. Lifestyle Factors
- Stress and anxiety affecting digestion
- Lack of physical activity leading to slow digestion
- Inadequate hydration, causing constipation and bloating
5. Medical Conditions
- Constipation: Trapped stool can cause bloating
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Gas buildup from acid reflux
- Gallbladder dysfunction: Issues with bile flow affecting digestion
Effective Strategies to Reduce Bloating and Gas
1. Dietary Changes
a) Eat Mindfully
- Chew food thoroughly to aid digestion
- Eat slowly to prevent swallowing excess air
- Avoid talking while eating
b) Identify and Avoid Trigger Foods
- Limit gas-producing foods like beans, onions, and dairy (if intolerant)
- Reduce processed foods that contain artificial sweeteners (sorbitol, xylitol)
- Be mindful of fiber intake – increase gradually to prevent bloating
c) Follow a Low-FODMAP Diet
- Avoid foods high in Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols (FODMAPs)
- Focus on easily digestible foods like bananas, rice, lean proteins, and cooked vegetables
d) Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water to aid digestion and prevent constipation
- Limit carbonated drinks that introduce excess gas into the gut
e) Incorporate Digestive-Friendly Foods
- Probiotics (yogurt, kefir, kimchi) to balance gut bacteria
- Ginger to ease digestion and reduce gas
- Peppermint tea to relax the digestive tract
2. Lifestyle Modifications
a) Regular Exercise
- Walking after meals helps move gas through the digestive tract
- Yoga poses like “wind-relieving pose” aid digestion
- Core-strengthening exercises improve gut motility
b) Manage Stress and Anxiety
- Practice deep breathing exercises to relax the digestive system
- Engage in meditation and mindfulness techniques
- Reduce caffeine and alcohol intake, which can worsen stress-related bloating
c) Improve Posture
- Sitting up straight while eating prevents swallowing air
- Avoid lying down immediately after meals to prevent acid reflux and gas buildup
d) Regulate Bowel Movements
- Maintain a fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation
- Establish a consistent bathroom routine
- Avoid holding in gas, as it can worsen bloating
3. Home Remedies for Immediate Relief
a) Herbal Teas
- Peppermint tea: Relaxes the gut and reduces bloating
- Ginger tea: Aids digestion and reduces inflammation
- Chamomile tea: Soothes the digestive system
b) Warm Water with Lemon
- Stimulates digestion and helps with detoxification
c) Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)
- Mix 1 tablespoon with warm water before meals to aid digestion
d) Activated Charcoal
- Helps absorb gas and reduce bloating (consult a doctor before use)
4. Medical Interventions
a) Over-the-Counter Remedies
- Simethicone: Helps break up gas bubbles in the stomach
- Lactase supplements: Aid digestion of dairy for lactose-intolerant individuals
- Digestive enzymes: Help break down food efficiently
b) When to See a Doctor
- Persistent bloating lasting more than two weeks
- Severe abdominal pain, weight loss, or blood in stool
- Symptoms of acid reflux, nausea, or vomiting
Preventive Measures for Long-Term Digestive Health
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet

- Include whole foods, fiber, and fermented foods
- Limit excessive sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats
2. Stay Active
- Engage in regular physical activity to keep the digestive system moving
3. Prioritize Gut Health
- Take probiotics to maintain a healthy gut microbiome
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotic use, which can disrupt gut bacteria
4. Monitor Food Intake
- Keep a food diary to track foods that trigger bloating and gas
5. Hydrate Properly
- Drink adequate water throughout the day to aid digestion
Bloating and gas can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but they can often be managed with dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. Identifying food triggers, maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress are essential steps to improve digestive health. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical advice is crucial to rule out underlying health conditions. By adopting these preventive measures and remedies, individuals can achieve long-term relief from digestive discomfort and enjoy better overall well-being.
Leave a Reply