The rapid advancements in digital technology have transformed how data is processed and stored. One of the most significant developments in recent years is edge computing, which is revolutionizing data management and computation. While cloud computing has dominated the IT landscape for over a decade, edge computing is emerging as a powerful complement to traditional cloud infrastructures. This article explores what edge computing is, its benefits, its relationship with cloud computing, and how businesses can leverage both for optimized performance.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed. Instead of sending data to centralized cloud data centers, edge computing processes it at or near the source, such as in IoT devices, local servers, or network gateways.
Key Characteristics of Edge Computing
- Proximity to Data Source – Processing occurs near the source of data generation, reducing latency.
- Real-time Processing – Enables quick decision-making without relying on cloud data centers.
- Decentralization – Unlike cloud computing, where data is managed in large, remote centers, edge computing distributes workloads across multiple locations.
- Bandwidth Optimization – Reduces the need for constant data transmission to centralized servers, saving network resources.
- Security and Privacy – Data processing occurs locally, reducing exposure to cyber threats during transmission.
Examples of Edge Computing in Action
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing helps self-driving cars process sensor data in real-time, reducing the risk of delays in decision-making.
- Smart Cities: Traffic management systems leverage edge computing to analyze congestion and adjust traffic signals dynamically.
- Industrial IoT: Manufacturing plants use edge computing to monitor equipment health, preventing downtime and optimizing maintenance.
- Healthcare Devices: Wearable health monitors analyze patient vitals in real-time and send alerts for abnormalities without relying on cloud processing.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including storage, processing, and networking—over the internet. It provides a centralized infrastructure where data and applications are stored and accessed remotely.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Centralized Storage and Processing – Data is processed in large data centers and accessed via the internet.
- Scalability – Organizations can scale resources up or down as needed without investing in physical infrastructure.
- Remote Access – Users can access cloud services from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cost Efficiency – Eliminates the need for on-premises hardware, reducing capital expenses.
- Security and Compliance – Cloud providers implement stringent security measures to protect data.
Examples of Cloud Computing in Action
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and YouTube use cloud computing to store and deliver content.
- Business Applications: Companies use cloud-based ERP and CRM software like Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics.
- Data Analytics: Enterprises run big data analytics on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
- Remote Work: Cloud-based collaboration tools like Google Drive and Microsoft Teams enable seamless remote work.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Location of Processing | Near the data source | Centralized data centers |
| Latency | Low (real-time processing) | Higher due to data travel time |
| Bandwidth Usage | Lower, as only essential data is sent to the cloud | Higher, as all data is transmitted to the cloud |
| Scalability | Limited to local infrastructure | Highly scalable with cloud resources |
| Security | Enhanced due to local processing | Strong security but vulnerable to cyber threats in transit |
How Edge Computing and Cloud Computing Work Together
While edge computing and cloud computing have distinct advantages, they are not mutually exclusive. Instead, they complement each other in a hybrid architecture.
Hybrid Cloud-Edge Architecture
A hybrid approach combines edge computing with cloud computing to balance efficiency, security, and scalability. Here’s how they work together:
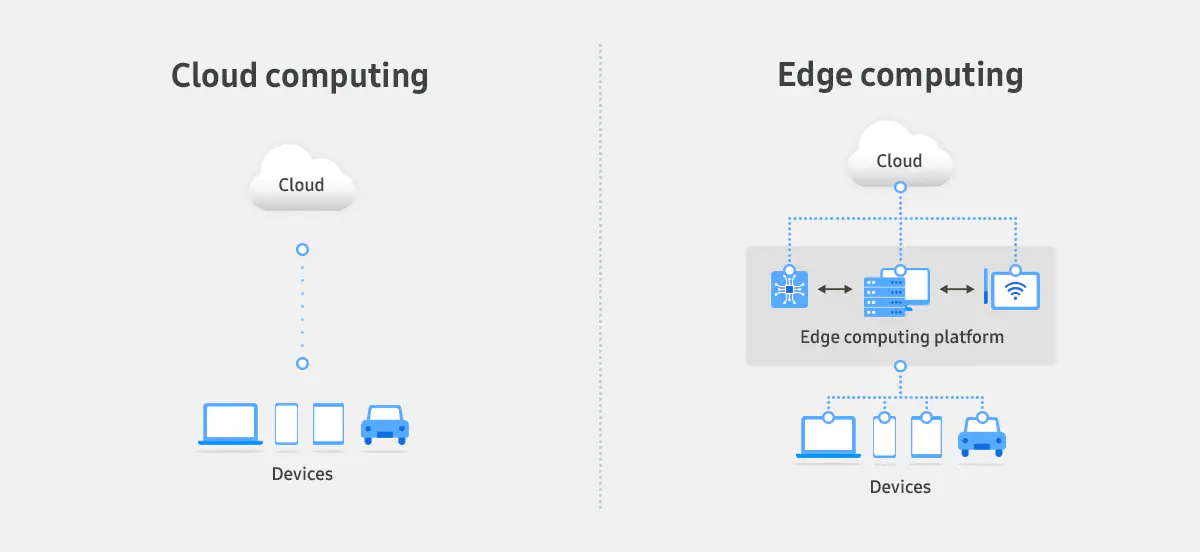
- Edge Processing for Real-Time Insights: Critical data is processed locally at the edge to ensure real-time responses.
- Cloud for Long-Term Storage and Analytics: Less time-sensitive data is sent to the cloud for deep analytics and historical records.
- Seamless Data Synchronization: Edge devices communicate with the cloud to share updates, software patches, and AI model improvements.
Use Cases of Cloud and Edge Integration
- Retail: Edge computing enables real-time customer tracking in stores, while cloud computing analyzes long-term purchasing trends.
- Healthcare: Edge devices monitor patients in hospitals, while cloud systems store patient records for research and compliance.
- Smart Homes: IoT-enabled home devices use edge computing for real-time automation, while cloud services manage device updates and user preferences.
- 5G Networks: Edge computing helps process data close to mobile users, while cloud computing handles complex AI-driven analytics.
Advantages of Using Edge and Cloud Computing Together
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing processes time-sensitive data locally, minimizing delays.
- Optimized Bandwidth Usage: Less essential data is offloaded to the cloud, reducing network congestion.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Critical data remains on local devices, reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
- Scalability: Cloud computing provides the flexibility to expand resources as needed.
- Improved Reliability: If cloud connectivity is lost, edge devices can continue operating autonomously.

Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, combining edge computing and cloud computing comes with challenges.
- Complex Infrastructure: Managing a hybrid system requires expertise in both edge and cloud technologies.
- Security Risks: While local processing reduces data exposure, edge devices can still be vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Data Synchronization: Ensuring real-time data consistency across edge and cloud environments is complex.
- Cost Considerations: Implementing edge computing requires investment in additional hardware and software.
The Future of Edge and Cloud Computing
The future of computing lies in the seamless integration of edge and cloud technologies. Emerging trends include:
- AI at the Edge: More devices will incorporate AI-driven decision-making without relying on cloud servers.
- 5G-Powered Edge Networks: The expansion of 5G will enhance edge computing capabilities with ultra-fast data transfer speeds.
- Edge-as-a-Service (EaaS): Cloud providers will offer managed edge computing solutions for businesses.
- Improved Cybersecurity Measures: Advanced encryption and blockchain technology will strengthen security in hybrid architectures.
Edge computing and cloud computing are reshaping how data is processed, stored, and utilized. While cloud computing remains a dominant force in the IT landscape, edge computing enhances real-time processing, security, and efficiency. By integrating both technologies, businesses can optimize performance, reduce latency, and improve scalability. As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, the synergy between edge and cloud computing will drive innovation across various sectors.

Leave a Reply