Technology has revolutionized the education sector in numerous ways, and one of the most groundbreaking innovations is 3D printing. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, allows users to create three-dimensional objects from digital models. This technology has found its way into classrooms, where it is reshaping the way students learn and interact with complex concepts. From enhancing creativity to bridging the gap between theory and practice, 3D printing is a game-changer in education.
This article explores the impact of 3D printing in education, its benefits, applications, challenges, and future prospects.
The Evolution of 3D Printing in Education
3D printing technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1980s. Initially, it was primarily used in industrial manufacturing and engineering fields. However, as the technology became more affordable and accessible, educational institutions began integrating it into their curricula.
Today, 3D printing is being utilized in various educational settings, from elementary schools to universities. With the growing emphasis on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education, schools are increasingly incorporating 3D printing into their teaching methodologies to provide hands-on learning experiences.

Benefits of 3D Printing in Education
1. Enhances Hands-On Learning
Traditional learning methods often rely on textbooks and lectures, which may not be effective for all students. 3D printing provides a hands-on learning experience that helps students grasp complex concepts more effectively. By creating tangible models, students can better understand subjects such as anatomy, physics, chemistry, and engineering.
2. Encourages Creativity and Innovation
3D printing allows students to bring their ideas to life. Whether designing prototypes, architectural models, or artistic sculptures, students can experiment with different designs and materials. This fosters creativity and innovation, encouraging students to think outside the box and develop problem-solving skills.
3. Bridges the Gap Between Theory and Practice
One of the biggest challenges in education is translating theoretical knowledge into practical applications. 3D printing bridges this gap by enabling students to create real-world objects based on their theoretical learning. For instance, engineering students can design and print mechanical parts, while biology students can print models of organs for study.
4. Supports Inclusive Education
3D printing has the potential to make education more inclusive by catering to students with special needs. For visually impaired students, 3D-printed tactile models can replace traditional 2D diagrams, helping them understand shapes, graphs, and biological structures through touch. This enhances their learning experience and makes education more accessible to all students.
How Teachers Can Use Data Analytics to Improve Their Teaching Methods
5. Cost-Effective Learning Materials
Schools often spend significant amounts on educational materials such as lab equipment, anatomical models, and architectural prototypes. 3D printing reduces costs by allowing institutions to produce these materials on-site at a fraction of the cost. Additionally, students can customize their learning materials based on their individual needs.
Applications of 3D Printing in Various Educational Fields
1. Science and Engineering
3D printing plays a crucial role in STEM education. Students can print and assemble mechanical parts, design robots, and create prototypes of machines. In physics, 3D-printed models can be used to demonstrate principles such as gears, levers, and pulleys. Chemistry students can print molecular structures to visualize atomic interactions.
2. Medicine and Biology
Medical and biology students benefit immensely from 3D printing technology. They can create anatomical models, such as human bones, hearts, and other organs, to better understand human physiology. This is particularly useful in medical training, where students can practice surgical procedures on 3D-printed models before working on real patients.
3. Architecture and Design
In architecture and design courses, students use 3D printing to create scale models of buildings, bridges, and landscapes. This helps them understand structural integrity, spatial relationships, and aesthetic design principles before moving to full-scale projects.
4. Art and Fashion
The artistic and fashion industries have also embraced 3D printing. Art students can experiment with new materials and design intricate sculptures that would be difficult to create using traditional methods. Fashion design students use 3D printing to produce unique clothing patterns, accessories, and footwear.
5. History and Archaeology
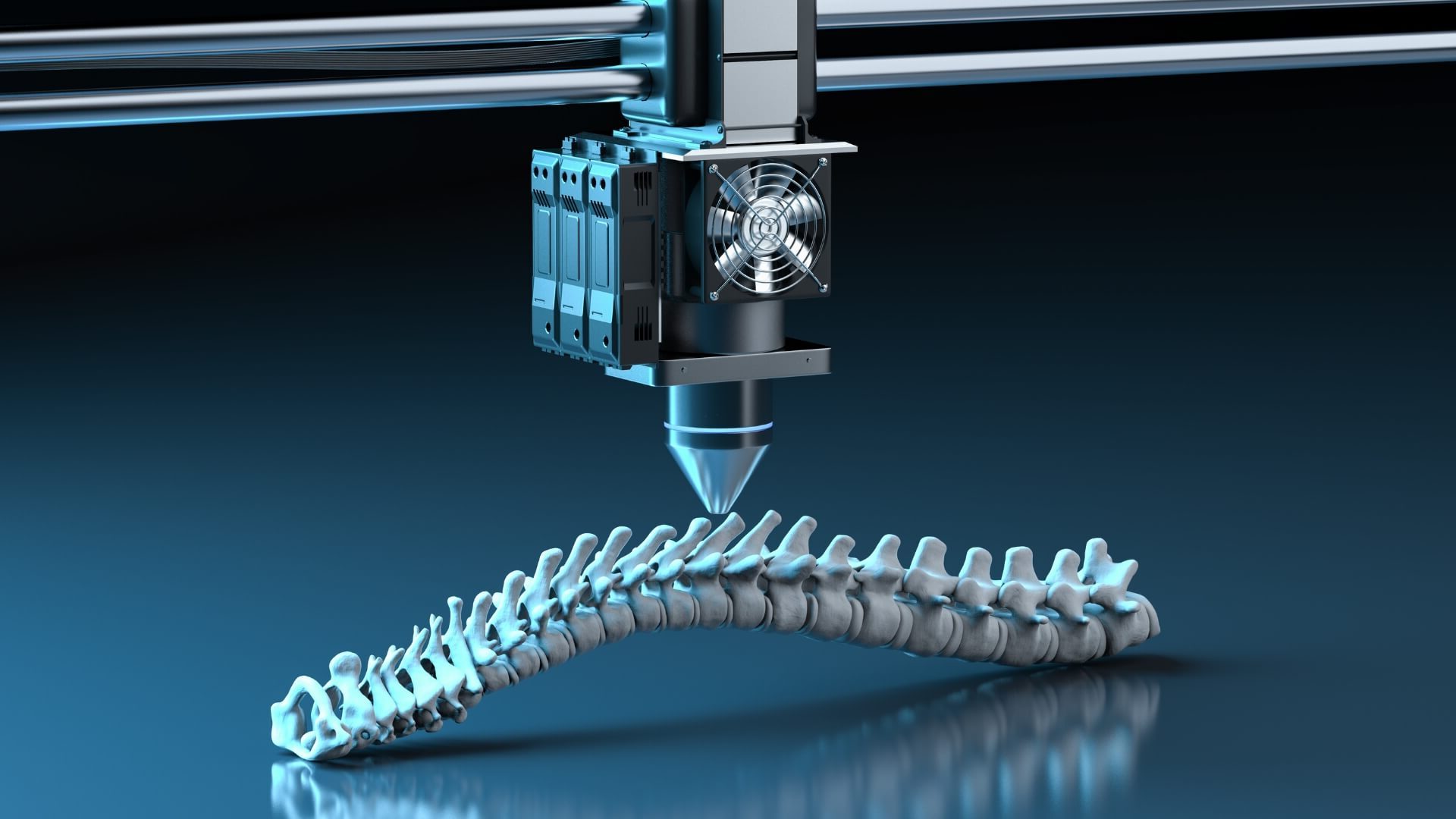
3D printing is revolutionizing the study of history and archaeology by allowing students to recreate ancient artifacts and fossils. This enables students to study historical objects in detail without the risk of damaging priceless artifacts. Museums and educational institutions use this technology to create replicas of rare artifacts for study and display.
Challenges of Implementing 3D Printing in Education
While 3D printing offers numerous benefits, there are challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption in education.
1. High Initial Costs
Although the cost of 3D printers has decreased over the years, acquiring high-quality printers and materials can still be expensive for some educational institutions. Additionally, maintenance and training costs may pose financial constraints.
2. Learning Curve and Technical Expertise
Teachers and students need to be trained to use 3D printing technology effectively. Learning how to operate 3D printers, design models, and troubleshoot issues requires time and effort. Schools must invest in training programs to ensure smooth integration into curricula.
3. Printing Time and Material Limitations
3D printing can be time-consuming, especially when creating complex models. Additionally, the range of materials available for printing in schools is often limited due to cost constraints. Some educational institutions may only have access to basic plastic filaments rather than advanced materials like metal or biodegradable composites.
4. Intellectual Property Concerns
As 3D printing enables students to replicate real-world objects, intellectual property rights can become an issue. Schools must educate students about copyright laws and ethical considerations when using 3D printing technology.
The Future of 3D Printing in Education
The future of 3D printing in education looks promising, with advancements in technology making it more accessible and efficient. Here are some potential developments:
1. Integration with Virtual and Augmented Reality
Combining 3D printing with virtual and augmented reality can enhance learning experiences. Students can design models in a virtual environment before printing them, providing a more immersive educational experience.
2. Expansion of Materials and Printing Capabilities
Future advancements in 3D printing materials will enable schools to print more diverse and durable objects. Biodegradable materials, flexible filaments, and even edible materials may become more widely available for educational purposes.

3. Personalized Learning and Customization
With AI-driven design tools, students will be able to create customized models tailored to their learning needs. This will enhance personalized education, allowing students to explore subjects at their own pace and according to their interests.
4. Increased Adoption in Developing Countries
As 3D printing technology becomes more affordable, developing countries can integrate it into their education systems, providing students with access to quality learning materials and opportunities for innovation.
3D printing is revolutionizing education by making learning more interactive, practical, and engaging. From science and engineering to art and medicine, its applications are vast and transformative. While challenges such as cost and technical expertise remain, continued advancements and increasing affordability will drive greater adoption in classrooms worldwide.
As educational institutions continue to embrace 3D printing, students will develop critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills that will prepare them for the future. By integrating this cutting-edge technology into education, we are shaping a new era of learning that empowers students to turn their ideas into reality.
Leave a Reply