Blockchain technology, the backbone of cryptocurrencies, has emerged as a transformative force across various industries. One of the most impacted sectors is traditional banking. The banking industry, known for its rigid structures and reliance on intermediaries, is now facing significant disruptions due to the decentralized, transparent, and secure nature of blockchain technology. This article delves into how blockchain is reshaping traditional banking systems, the benefits and challenges associated with its adoption, and the future implications of this technology in the financial sector.
The Traditional Banking System: Challenges and Limitations
Before understanding blockchain’s impact, it is essential to recognize the inherent challenges within traditional banking systems:
- High Transaction Costs: Banks act as intermediaries for financial transactions, often charging high fees for domestic and international payments.
- Slow Transaction Processing: Cross-border transactions take days to process due to multiple intermediaries and regulatory procedures.
- Lack of Transparency: Centralized banking systems are prone to opacity, which increases the risk of fraud and corruption.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Banks are prime targets for cyberattacks, and centralized databases are vulnerable to breaches.
- Limited Accessibility: Many unbanked populations lack access to banking services due to geographical and financial barriers.
- Inefficiency in Loan Processing: The traditional banking loan approval process is cumbersome, requiring extensive paperwork and credit history checks.
Blockchain technology addresses these challenges by introducing a decentralized, secure, and transparent financial ecosystem.
How Blockchain is Disrupting Traditional Banking
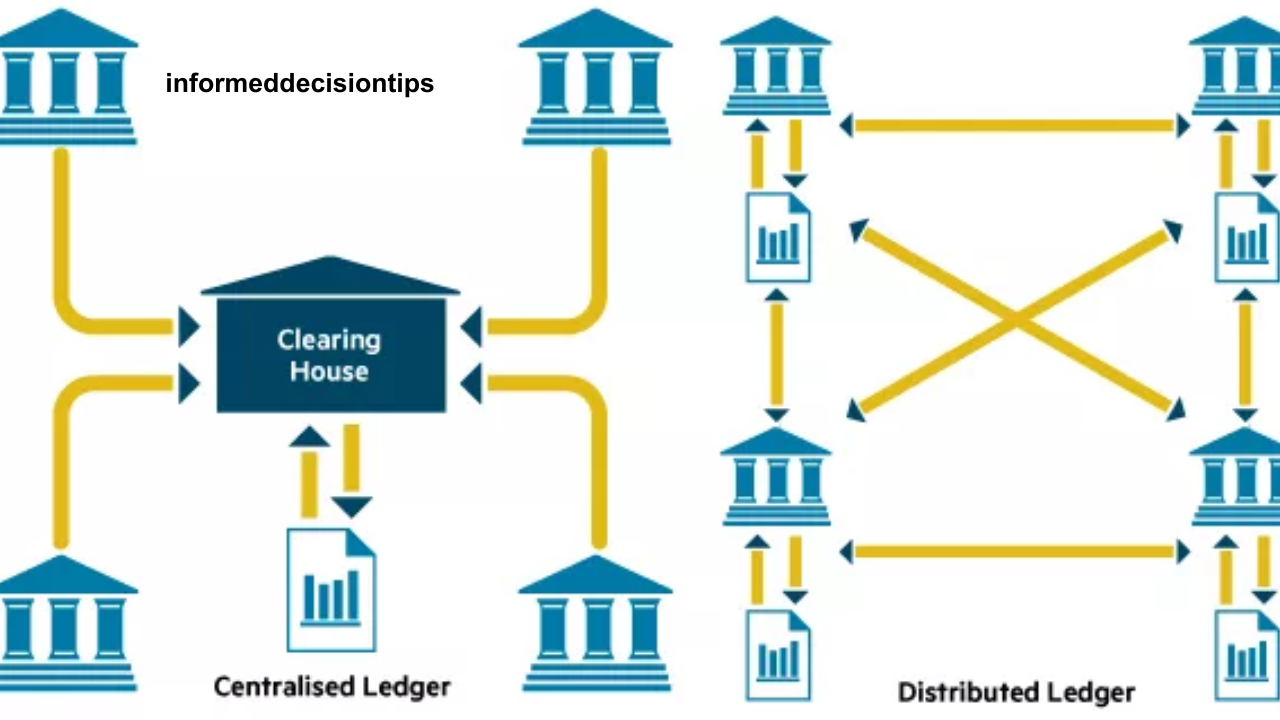
1. Decentralization and Elimination of Intermediaries
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks and clearinghouses. Peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions allow individuals to send and receive funds directly, reducing reliance on third parties. This not only lowers transaction costs but also enhances the speed of financial transactions.
2. Faster and Cost-Effective Cross-Border Transactions
Traditional cross-border transactions can take several days and involve multiple banks and clearinghouses, resulting in high fees. Blockchain-based solutions, such as Ripple’s XRP, facilitate real-time international payments with significantly lower costs. These transactions settle in seconds, providing a more efficient alternative to traditional banking systems.
3. Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Blockchain employs cryptographic security measures, making it nearly impossible for hackers to alter transaction data. The distributed ledger system ensures that every transaction is recorded and validated by multiple nodes, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Additionally, smart contracts enhance security by automating transaction execution based on predefined conditions.
4. Transparency and Trust
One of blockchain’s core advantages is transparency. All transactions are recorded on an immutable ledger, making it easier to track financial activities and reduce fraudulent activities. This transparency fosters trust among customers, businesses, and financial institutions.
5. Increased Financial Inclusion
According to the World Bank, around 1.7 billion adults globally remain unbanked. Blockchain offers a solution by providing decentralized financial services accessible via mobile devices. Cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based banking platforms enable individuals in underbanked regions to store, send, and receive money without needing a traditional bank account.
6. Improved Loan and Credit Systems
Traditional lending requires extensive credit checks and intermediary involvement, which can delay loan approvals. Blockchain introduces decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms that offer loans without intermediaries. Smart contracts execute loan agreements automatically, reducing paperwork and ensuring faster loan approvals.
7. Tokenization of Assets
Blockchain enables the tokenization of assets, allowing real estate, stocks, and commodities to be represented as digital tokens. This enhances liquidity and makes investment opportunities more accessible to a global audience. Traditional banks may struggle to offer such seamless asset management solutions.
8. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Many central banks are exploring the development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) to leverage blockchain’s efficiency. CBDCs can provide a more secure and efficient digital payment system, reducing dependence on commercial banks. Countries such as China (with its Digital Yuan) and the European Union are actively testing blockchain-based digital currencies.
9. Smart Contracts for Automation
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements stored on the blockchain. These contracts automate financial transactions, reducing administrative costs and improving efficiency. Banks can use smart contracts for loan processing, insurance claims, and compliance verification, ensuring faster execution with minimal human intervention.

10. Regulatory Compliance and Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Blockchain’s transparent ledger facilitates compliance with regulatory frameworks, including AML and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. Regulatory authorities can access immutable transaction records to detect suspicious activities, reducing financial crimes and enhancing compliance efficiency.
Challenges and Barriers to Blockchain Adoption in Banking
Despite its potential, blockchain adoption in the banking sector faces several challenges:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments and regulatory bodies are still developing legal frameworks for blockchain and cryptocurrencies, leading to uncertainty in adoption.
What is Blockchain? A Beginner’s Guide to Decentralized Technology
- Scalability Issues: Blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, struggle with scalability due to transaction speed limitations and high energy consumption.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Traditional banks rely on legacy infrastructure that is not easily compatible with blockchain technology.
- High Initial Costs: Implementing blockchain solutions requires significant investment in technology and expertise.
- Security Concerns in DeFi: While blockchain enhances security, DeFi platforms are still vulnerable to smart contract bugs and hacking attempts.
- Consumer Awareness and Adoption: Many consumers and businesses are still unfamiliar with blockchain, making widespread adoption challenging.
The Future of Blockchain in Banking
The banking industry is gradually embracing blockchain, and its future implications are promising:
![]()
- Mainstream Adoption of CBDCs: More central banks will launch digital currencies, integrating blockchain into national economies.
- Enhanced Regulatory Frameworks: Governments will establish clearer regulations, fostering blockchain’s integration into traditional finance.
- Improved Blockchain Scalability: Advancements in blockchain protocols, such as Ethereum 2.0 and Layer 2 solutions, will enhance transaction speed and efficiency.
- Decentralized Banking: More individuals will adopt decentralized financial services, reducing reliance on traditional banks.
- Collaboration Between Banks and Blockchain Firms: Banks will partner with blockchain startups to innovate and modernize financial services.
- AI and Blockchain Integration: Artificial intelligence (AI) will enhance blockchain’s capabilities in fraud detection, risk management, and automated decision-making.
Blockchain technology is disrupting traditional banking systems by introducing decentralization, transparency, security, and efficiency. While challenges remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the limitations. As banks and financial institutions adapt to this transformation, blockchain will continue to reshape the global financial landscape, paving the way for a more inclusive, secure, and efficient banking ecosystem. The traditional banking model must evolve and integrate blockchain-driven solutions to remain relevant in this rapidly changing digital economy.

Leave a Reply