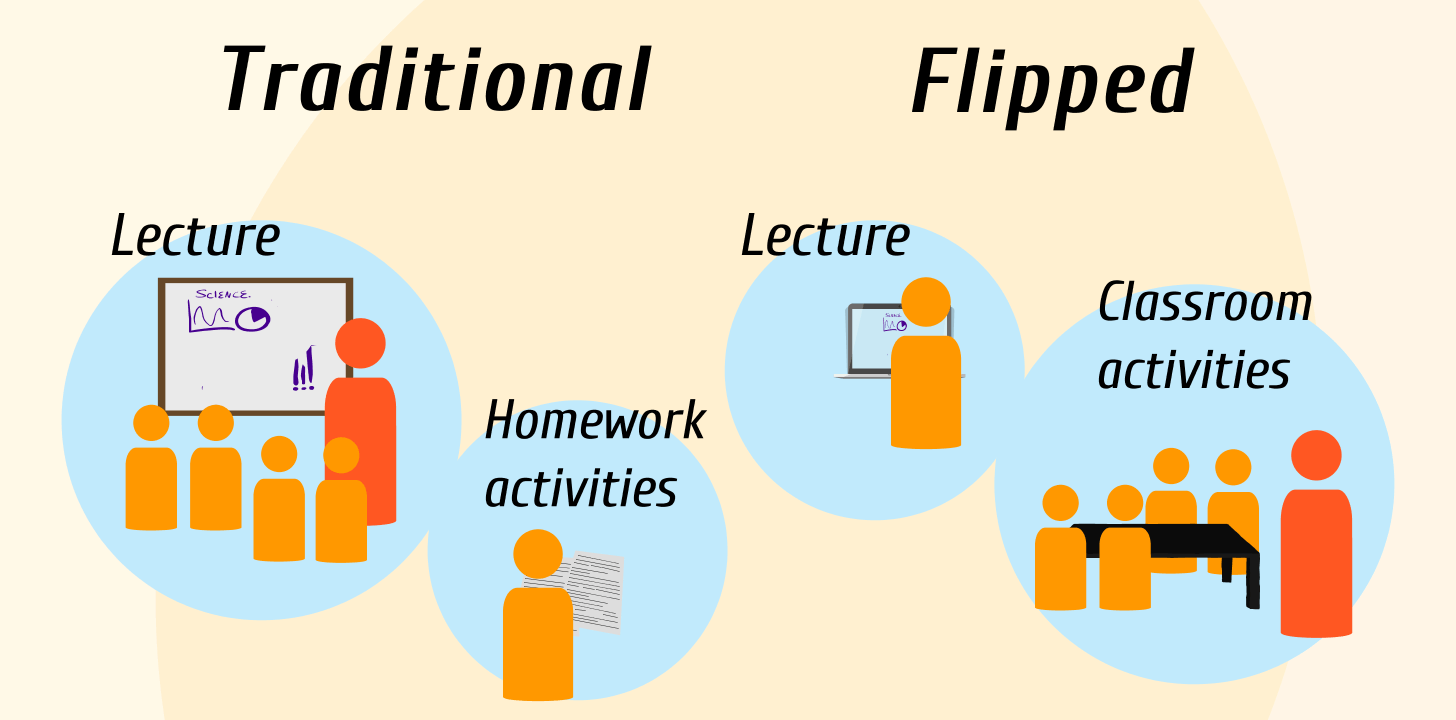
The traditional education system follows a model where students learn new concepts in the classroom through lectures and then complete assignments or exercises at home. However, with the advancement of technology and a better understanding of how students learn, a new approach called the “Flipped Classroom Model” has emerged. This model reverses the conventional learning process, allowing students to first explore concepts at home and then apply them in a classroom setting through interactive activities.
The flipped classroom has gained popularity among educators as a student-centered learning method that promotes engagement, collaboration, and deeper understanding. In this article, we will explore what the flipped classroom model is, how it works, its advantages and challenges, and how educators can implement it effectively.
What Is the Flipped Classroom Model?
The flipped classroom model is a pedagogical approach where traditional teaching methods are reversed. Instead of students receiving direct instruction during class time and working on assignments at home, they are introduced to new concepts before class through online videos, readings, or other digital resources. Then, during class time, students engage in discussions, problem-solving, group activities, and hands-on learning under the guidance of their teacher.

This approach shifts the focus from passive learning (listening to lectures) to active learning (practicing and applying knowledge). It allows students to take control of their learning pace and promotes a deeper understanding of the material through interactive class sessions.
How Does the Flipped Classroom Model Work?
The flipped classroom model follows a structured process to maximize student engagement and learning outcomes. Below are the key steps in how it works:
1. Pre-Class Learning
Before attending the class, students are required to engage with instructional materials. These materials may include:
- Pre-recorded video lectures: Teachers create or curate educational videos covering key concepts.
- Online readings and articles: Supplementary reading materials provide additional context.
- Interactive content: Online quizzes, simulations, or educational apps reinforce learning.
- Guided questions: Reflection questions help students think critically about the content.
This phase ensures that students arrive in class with a foundational understanding of the topic, ready to engage in active learning.
2. In-Class Activities
During class time, students participate in various interactive and collaborative activities that reinforce their learning. These activities may include:
- Group discussions and debates: Encouraging students to express their perspectives and analyze different viewpoints.
- Problem-solving exercises: Working on complex problems with peer collaboration and teacher support.
- Hands-on experiments: Conducting scientific experiments or practical applications of theories.
- Case studies and real-world applications: Connecting theoretical concepts with real-world scenarios.
- Peer teaching: Encouraging students to explain concepts to each other to reinforce their understanding.
The teacher acts as a facilitator, guiding students and addressing misconceptions rather than simply delivering information.
3. Post-Class Assessment and Feedback
After class, students are encouraged to review their learning through assessments and feedback. This phase includes:
- Quizzes and tests: Online or in-class assessments to gauge understanding.
- Reflection assignments: Writing summaries or reflections to solidify knowledge.
- Teacher feedback: Individualized or group feedback on student performance and progress.
This final step ensures continuous improvement and reinforces learning through iterative practice.
Benefits of the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model offers several advantages for students and educators alike:
1. Increased Student Engagement
Since class time is dedicated to active learning, students are more engaged in the process. Interactive activities make learning more enjoyable and meaningful.
2. Personalized Learning Pace
Students can watch pre-class videos and review materials at their own pace. This flexibility accommodates different learning speeds and styles.
3. Improved Comprehension and Retention
Engaging in active problem-solving and discussions helps students retain information better compared to passive listening.
4. Greater Student-Teacher Interaction
Teachers spend more time addressing individual student needs and clarifying doubts rather than simply delivering lectures.
5. Enhanced Collaboration and Critical Thinking
Group activities and discussions encourage teamwork, communication, and critical thinking skills—essential for success in real-world scenarios.
6. Efficient Use of Classroom Time
Instead of spending time on basic instruction, class time is used for deeper exploration and higher-order thinking activities.
7. Accessibility and Reusability of Learning Materials
Recorded lectures and online resources can be accessed anytime, allowing students to revisit concepts as needed.
Challenges of the Flipped Classroom Model
While the flipped classroom model has numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges:
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Career Guidance and Counseling
1. Digital Divide and Access to Technology
Not all students have access to reliable internet and digital devices, which can create disparities in learning.
2. Increased Teacher Preparation Time
Creating high-quality instructional videos and materials requires additional effort and time from educators.
3. Student Resistance to Change
Some students may struggle with self-paced learning or resist taking responsibility for pre-class preparation.
4. Classroom Management Challenges
Facilitating active learning sessions requires effective classroom management skills to ensure productivity.
5. Assessment Difficulties
Measuring student learning in a flipped model may require alternative assessment strategies beyond traditional exams.
How to Implement a Flipped Classroom Effectively
Educators can adopt best practices to successfully implement the flipped classroom model:
1. Start Small and Gradually Scale Up
Begin with a single flipped lesson before transitioning to a fully flipped classroom approach.
2. Use High-Quality Digital Resources
Ensure that instructional videos and materials are engaging, concise, and aligned with learning objectives.
3. Provide Clear Guidance and Expectations
Clearly communicate to students what they need to do before, during, and after class to avoid confusion.
4. Encourage Accountability
Incorporate quizzes or short assignments to ensure students complete pre-class learning activities.

5. Foster an Interactive Classroom Environment
Plan engaging, hands-on activities that encourage participation and collaboration.
6. Leverage Technology
Utilize online platforms, discussion forums, and learning management systems to support the flipped model.
7. Seek Continuous Feedback
Gather feedback from students to refine and improve the flipped classroom approach over time.
Real-World Applications of the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model is widely used in various educational settings:
1. K-12 Education
Many schools integrate the flipped model to enhance engagement and comprehension in subjects like math, science, and language arts.
2. Higher Education
Colleges and universities use flipped classrooms to facilitate deeper discussions and research-based learning.
3. Professional Training
Corporations and organizations implement flipped learning for employee training and skill development programs.
4. Online and Hybrid Learning
Flipped learning is commonly used in online courses to make virtual education more interactive and effective.
The flipped classroom model is revolutionizing the way education is delivered, making learning more engaging, student-centered, and effective. By shifting direct instruction outside the classroom and focusing on interactive, hands-on learning during class time, educators can create an environment that promotes critical thinking, collaboration, and deep understanding.
While challenges exist, they can be mitigated through careful planning, technology integration, and ongoing feedback. As education continues to evolve, the flipped classroom model remains a powerful tool for fostering meaningful and impactful learning experiences.
Leave a Reply