In today’s digital world, cyber threats are constantly evolving, making it essential to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information. One of the most effective methods to enhance security is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA provides an additional layer of security beyond just a username and password, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult for cybercriminals. This article explores the concept of MFA, how it works, its benefits, and why it is crucial for securing online accounts and sensitive data.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
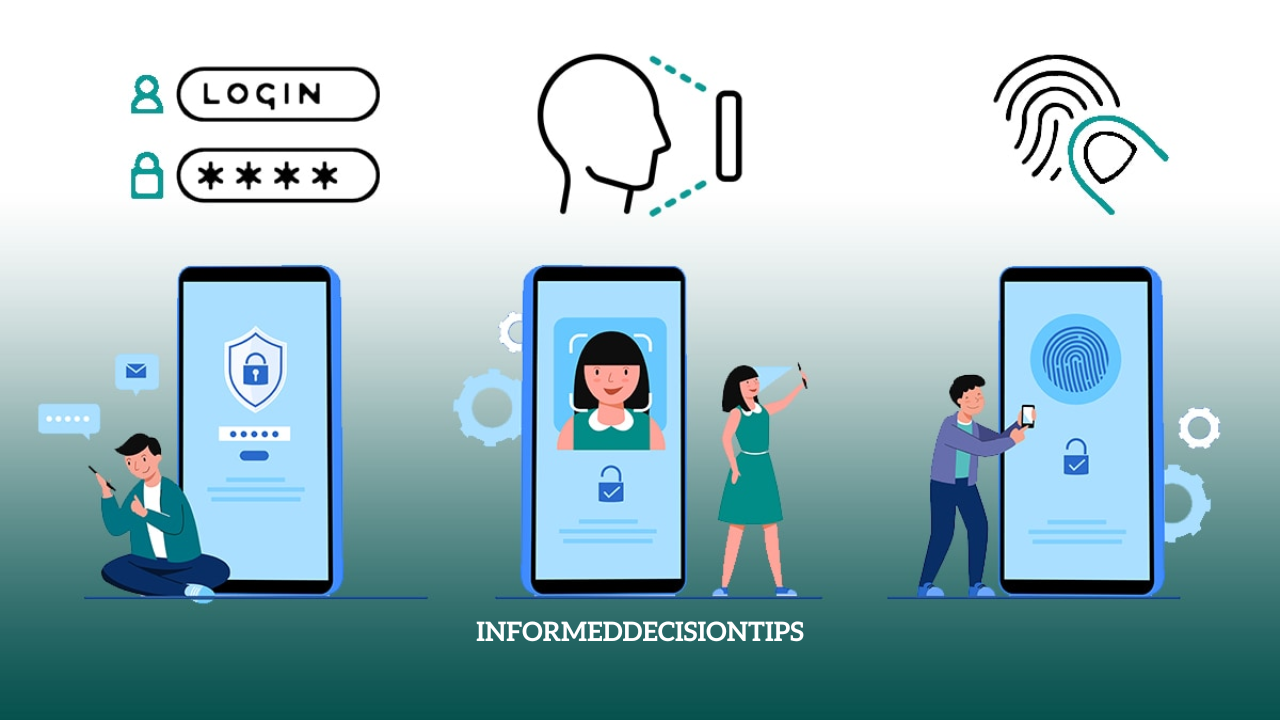
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to an account, system, or application. Unlike single-factor authentication (SFA), which relies solely on a password, MFA enhances security by combining two or more independent authentication factors. These factors typically fall into three categories:

- Something You Know – Information the user knows, such as a password, PIN, or security question answer.
- Something You Have – A physical device or token, such as a smartphone, security key, or smart card.
- Something You Are – Biometric data, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns.
By requiring multiple factors, MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if one factor is compromised.
How Multi-Factor Authentication Works
MFA operates by requiring users to provide at least two of the three authentication factors before granting access. The process generally follows these steps:
- User Credentials Entry: The user enters their username and password (something they know).
- Additional Verification: The system prompts the user for an additional authentication factor, such as a one-time password (OTP) sent to their mobile device (something they have) or a fingerprint scan (something they are).
- Access Granted: If both authentication factors are verified successfully, the user gains access to the system.
For example, when logging into an online banking account, a user may need to enter their password and then confirm their identity by entering a code sent to their registered mobile phone.
Types of Multi-Factor Authentication
There are several types of MFA mechanisms used across various platforms to enhance security. Some common MFA methods include:
- One-Time Passwords (OTPs) – OTPs are temporary passcodes sent via SMS, email, or an authenticator app.
- Hardware Tokens – Physical devices that generate authentication codes, such as YubiKeys or RSA tokens.
- Software-Based Authentication – Apps like Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator generate time-sensitive codes.
- Biometric Authentication – Fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or voice recognition.
- Push Notifications – Notifications sent to a trusted device for user approval.
- Behavioral Analysis – Systems that monitor user behavior, such as typing speed and mouse movements, to verify identity.
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication
1. Enhanced Security
Passwords alone are often weak and vulnerable to hacking methods like phishing, brute force attacks, and credential stuffing. MFA adds an extra layer of protection, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
2. Mitigating Phishing Attacks
Phishing scams trick users into revealing their login credentials. Even if a hacker obtains a user’s password through phishing, they would still need the second authentication factor to access the account.
3. Compliance with Security Regulations
Many industries and regulatory bodies, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, require organizations to implement MFA to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance.
4. Protecting Sensitive Information
MFA is crucial for protecting personal and business data, preventing data breaches, and ensuring that only authorized users can access critical systems.
5. Preventing Account Takeovers
Cybercriminals often use stolen credentials to take over accounts. MFA helps prevent unauthorized access even if login credentials are compromised.
6. Securing Remote Access
With the rise of remote work, MFA is essential for securing remote access to corporate networks, reducing the risk of cyberattacks targeting remote employees.
Challenges and Limitations of MFA
While MFA is highly effective, it is not without challenges:
- User Convenience – Some users find MFA cumbersome and time-consuming.
- Potential Device Loss – Losing an authentication device, such as a phone or hardware token, can lock users out of their accounts.
- Phishing of Second Factor – Some advanced phishing attacks can trick users into revealing their second authentication factor.
- Cost of Implementation – Businesses may face costs associated with deploying MFA solutions.
- System Integration Issues – Some legacy systems may not support MFA, requiring additional upgrades.

Best Practices for Implementing MFA
To maximize the effectiveness of MFA, organizations and individuals should follow these best practices:
- Use Strong Authentication Methods – Opt for secure MFA methods like biometric authentication and authenticator apps over SMS-based OTPs.
- Enable MFA on All Critical Accounts – Implement MFA on banking, email, cloud storage, and corporate accounts.
- Educate Users – Train employees and users on the importance of MFA and how to recognize phishing attempts.
- Use Adaptive MFA – Implement risk-based authentication that adjusts security measures based on user behavior and login patterns.
- Have Backup Authentication Options – Provide alternative methods for account recovery in case the primary authentication factor is lost.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure that significantly enhances account and data protection by requiring multiple forms of verification. In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, relying solely on passwords is no longer sufficient. MFA mitigates risks associated with phishing, data breaches, and unauthorized access, making it an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies. While there may be challenges in implementing MFA, its benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, ensuring that individuals and organizations remain secure in the digital world. By adopting MFA, businesses and users can safeguard their sensitive information, maintain compliance, and build a stronger security posture against cyber threats.
Leave a Reply